PURE RELIEF HEEL SPUR FORMULA
What are Calcaneal or heel spurs?
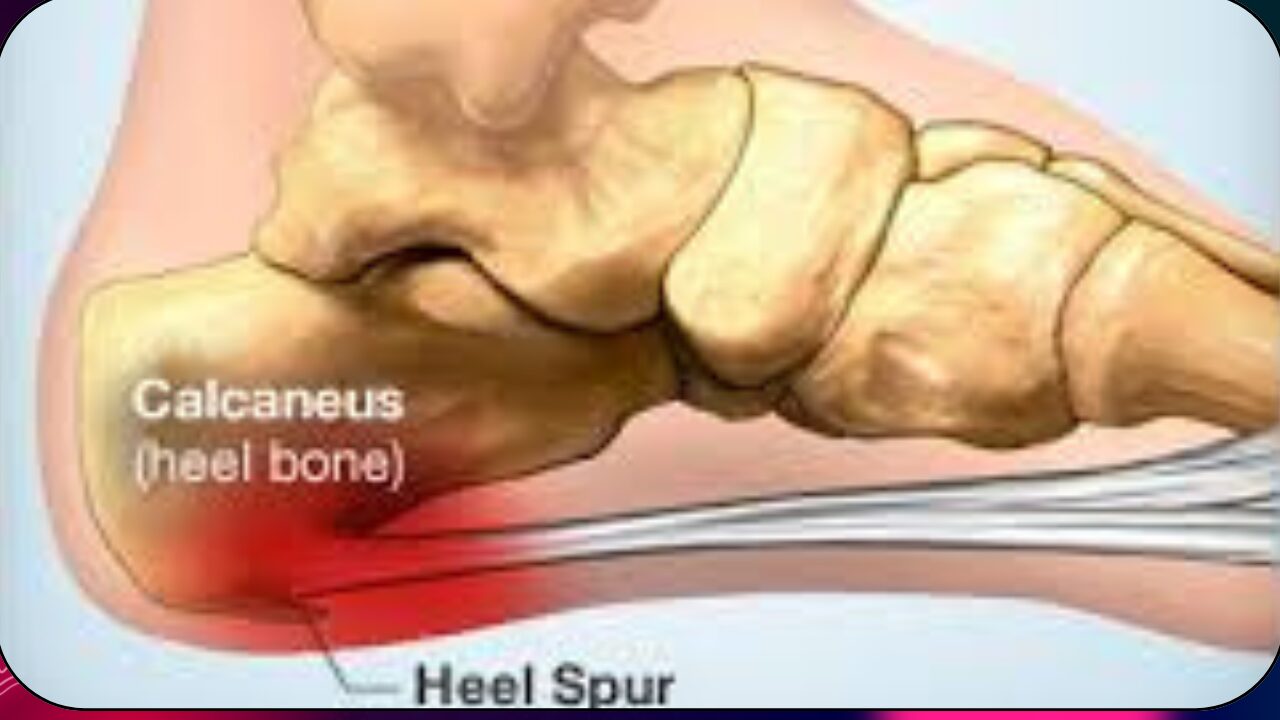
A calaneal spur (or heel spur) is a bony spur (osteophyte) or projection on the back or underside of the heel bone (Calcaneus bone).
A spur which develops on the underside of the calcaneus (heel) may also be associated with inflammation of the plantar fascia (band of tissue which connects the calcaneus or heel bone with the toes) and is considered to be one of the most common orthopedic complaints.
A spur on the back of the calcaneus or heel occurs where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel. It is also known as ‘Achilles Calcific Insertional Tendinosis (AICT)’.
Symptoms caused by Calcaneal Spurs
Not all heel spurs cause symptoms and are sometimes routinely diagnosed during an X-Ray. The symptoms, if any, can range from mild to sever and varies depending on the location of the spur.
Spurs formed on the underside of the heel cause pain and tenderness by stepping down on the heel. This pain is usually more in the morning on first stepping your heel on the floor and also increases with walking.
Spurs on the back of the heel are associated with inflammation of the Achilles tendon causing pain located on the back side of the heel.
Heel Spur Types
There are mainly 2 types of heel spur which are as follows: –
1. Type A Heel Spur
Type A Heel spurs are found superiorly on the plantar fascia.
In this type, the spurs under the sole are associated with plantar fasciitis.
In this type of heel spur, the apex of the spur lies either within the origin of the planar fascia or just
superior to the brevis muscles.
2. Type B Heel Spur
In Type B, the Heel spur extends slightly forward from the plantar fascia.
The patient suffers from severe dull aching pain even in the muscles.
Mostly this type of heel pain occurs in middle-aged people and athletes. There is excessive pain in this type of spur from the mechanical support also patient doesn’t get any relief and the condition goes into inflammation.
Here are some commonly recommended homeopathic remedies for heel spurs:
1. Rhus Toxicodendron: This is often suggested for pain that is worse after resting and improves with movement. It also aid in lowering inflammation and edema.
2. Calcarea Fluorica:Hard Rocky limbs on the soles of the feet. Used for conditions involving bone and tendon issues, including heel spurs.
3. Arnica Montana: It is often suited to patients suffering from heel spur when patients feels numbness and sensitive to cold air.Known for its anti-inflammatory properties,it is used for pain and soreness.
4. Bryonia: Recommended for sharp, stabbing pain that worsens with movement.
5. Ruta Graveolens: Often used for injuries to tendons and ligaments, particularly when the pain is worse with stretching.
6. Silicea: Utilized for conditions where there is chronic pain and sensitivity in the affected area.
7. Symphytum: In case of plantar fascitis accompanied by bone fracture and discomfort this remedy is useful.Known for its healing properties for bones, it can be useful for bone spurs
Some common risk factors are:
1. There are walking abnormalities with excessive stress and pain on the heel bone, ligaments, tendons, and nerve near the heel.
2. Pain may increase due to running or jogging on a hard surface.
3. The patient may have excessive weight also due to obesity.
4. If the patient is suffering from diabetes, thyroid, or any other hormonal imbalance may have a high risk of getting heel spur.
5. The person who has flat feet or a high arch may also have the risk of having heel spur.
6. The person who spends most of the day standing soo long and has less physical activity.
7. Wear torn shoes which causes uncomfortable while walking.
Diagnosis of Heel Spur
The following diagnostics test for heel spur are as follows: –
1. X-Ray
X-ray is the best diagnosis which can be done easily and of low cost.
It is the first popular line of defense to find the cause of foot painting. X-ray detects the presence of heel spur with calcium deposition around the fatty pad of the heel.
2. Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography is an easy and quick diagnostic test that helps in detecting the soft tissue in the foot. It also shows whether the fatty pad looks normal or not.
3. MRI
MRI helps to detect the cross-section images of bones, tendons, ligaments, injuries, lesions, cysts, etc.
It detects the pinpoint plantar tears or ruptures of tendons, ligaments, etc. It sometimes also helps in detecting Achilles tendonitis.
4. CT SCAN
CT Scan is a special type of x-ray used to detect the detailed cross-section of the foot. It is typically used to diagnose plantar fasciitis and tumor on the heel or calcaneal. From a CT Scan patient gets a small amount of radiation.
There are many ways to manage such as: –
1. First thing to keep in mind is to avoid a sedentary lifestyle and routine.
2. Eat nutritious and healthy food. Add green vegetables and fruits necessary for the diet.
3. Do not skip medicines for other health problems.
4. Maintain proper hygiene and cleanliness daily.
5. Avoid smoking and drinking. This may lead to severe health problems.
6. Add physical activity and yoga to your routine.
7. Avoid standing and walking for long hours.
8. Appy ice packs for 20 minutes 3 times a day to avoid heel spur and pain.
9. Wear footwear or shoes which are comfortable and support arches while walking and from the bottom of your feet.
10. Add massage to the affected area with a slight hand.