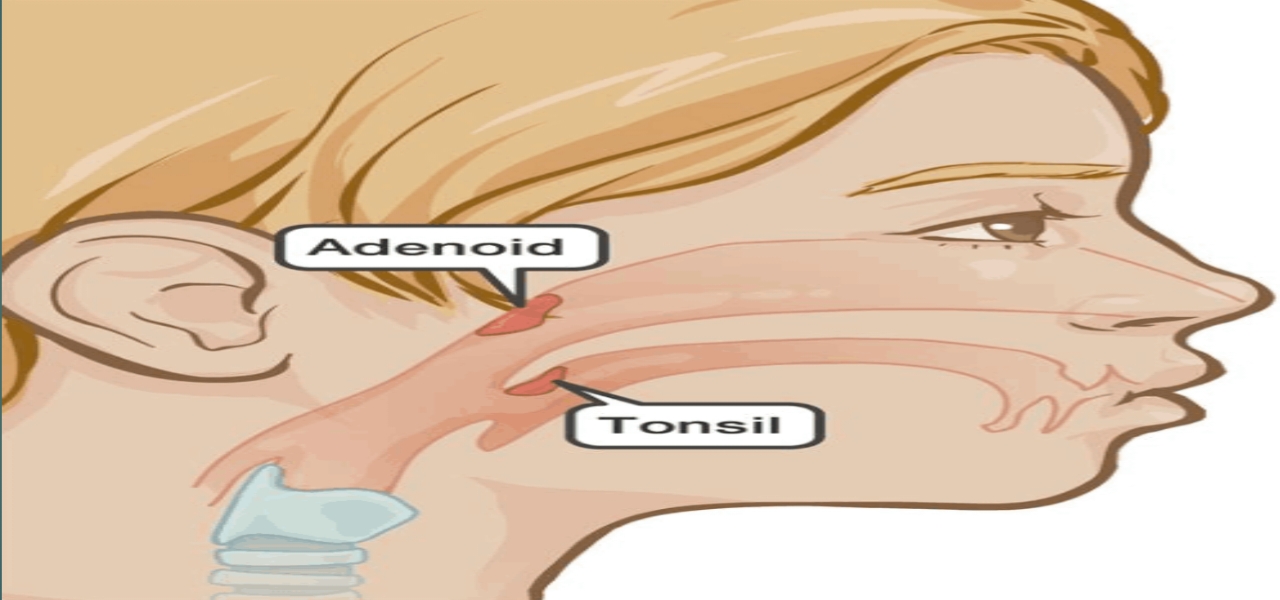
Adenoids are an essential part of the immune system, playing a key role in protecting the body by trapping harmful bacteria and viruses that enter through the nose and mouth. However, when the adenoids become enlarged, they can partially or completely block the airway, causing a range of symptoms like mouth breathing, snoring, sleep apnea, nasal congestion, and difficulty swallowing. This blockage not only disrupts normal breathing but can also lead to noticeable changes in the facial structure, particularly in children.
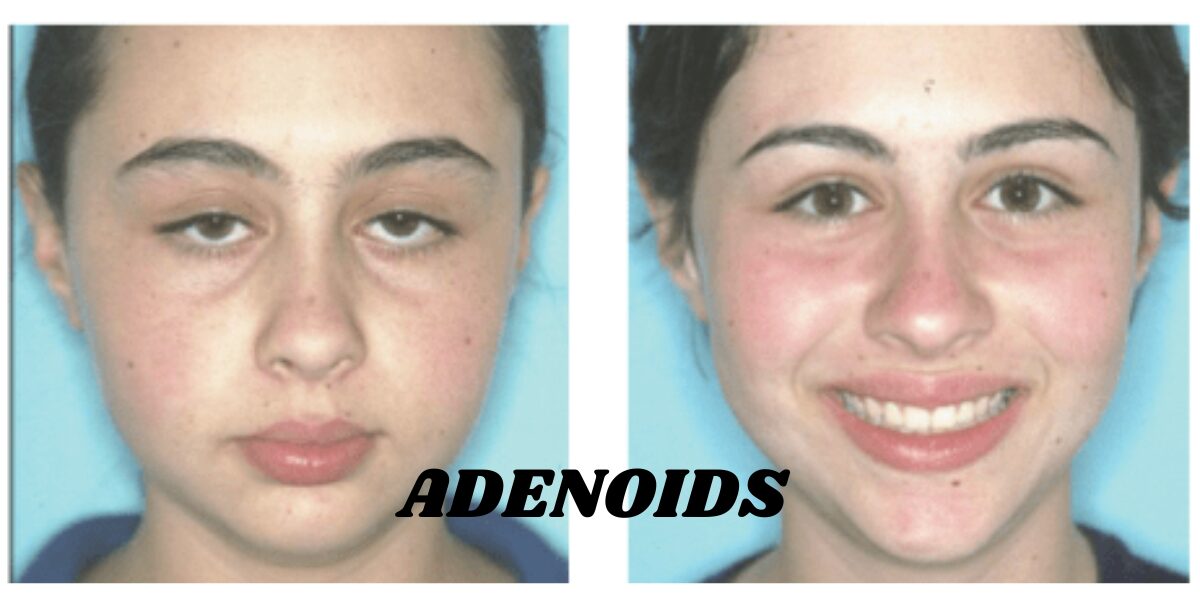
A condition called adenoid face may develop due to persistent blockage. It results in a long, narrow face, a high-arched palate, an open mouth, and crowded teeth. Other signs include a flattened appearance, a prominent forehead, and sunken eyes. Most commonly affecting children between the ages three and seven, this happens because their adenoids are relatively larger in proportion to their airways. Besides physical changes, problems like speech problems, delayed language development, and even poor growth due to reduced oxygen intake during sleep are possible. In such cases, treatment often involves the removal of adenoids through a surgical procedure called an adenoidectomy.
CAUSES OF ADENOIDS
- Enlarged adenoids are the main cause of an adenoid face. These structures, which are part of the immune system, help the body fight off infections but can become enlarged due to chronic infection or inflammation. This swelling can block the airway, leading to significant obstruction and changes in the facial structure.
- Chronic mouth breathing
A child with chronic mouth breathing, often caused by altered breathing patterns from an obstructed airway, may develop issues with the tongue and muscles, which can lead to dental problems like an open bite or crowded teeth.
- Sleep apnea,
Another consequence of enlarged adenoids is sleep apnea, where breathing stops and starts during sleep. This condition can result in serious health problems like fatigue, poor concentration, and developmental delays.
- Children with chronic obstruction of the airway may experience impaired facial growth and development, contributing to the distinctive features of an adenoid face. Recognizing these patterns early can prevent further complications.
GENETICS
Some cases of adenoid face may be linked to genetics. Certain genetic conditions, such as Pierre Robin Syndrome, can cause the tongue to be positioned too far back in the mouth, leading to chronic obstruction of the airway. This obstruction can result in significant changes in facial growth and overall development. When these genetic factors combine with structural challenges, the distinctive features of adenoid face become more pronounced.
Environmental factors.
Other causes include allergies and environmental factors. Allergies can lead to inflammation in the nasal cavity and adenoids, resulting in enlargement, nasal congestion, and difficulty breathing through the nose. Exposure to secondhand smoke, pollution, and other irritants can damage the respiratory system and contribute to enlarged adenoids and related symptoms. These triggers create a cycle of airway obstruction that can worsen over time if untreated.
SYMPTOMS OF ADENOIDS
The adenoids, a small mass of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the nasal cavity, play an essential role in defending against infections. However, when they become enlarged, they can lead to a variety of symptoms, many of which impact breathing, sleep, and overall development.
1 .One common sign is mouth breathing, particularly if it becomes chronic. An obstructed airway makes it hard for a person to breathe through the nose, forcing them to rely on breathing through their mouth. This habit can worsen over time and may contribute to other complications like changes in the facial structure, including an elongated face, a high-arched palate, and crowded teeth.
Children with sleep apnea may face serious health problems like fatigue, poor concentration, and even developmental delays due to interrupted rest.
3. Nasal congestion often accompanies enlarged adenoids, making it difficult to breathe through the nose comfortably. In some cases, this can also result in ear infections, as the blocked airway causes fluid to accumulate in the middle ear, increasing the risk of recurring infections.
4. The structural impact of enlarged adenoids can include a flat nasal bridge, sunken eyes, and an open-mouth posture, all of which contribute to the characteristic adenoid face. These changes, often gradual, are more pronounced in children, especially when the condition persists untreated.
5. Lastly, enlarged adenoids can lead to speech problems and difficulty swallowing. Obstruction in the airway can make it hard to produce sounds correctly or maintain a normal swallowing function, further complicating everyday activities and communication.
RISK FACTORS
The likelihood of developing adenoid face is influenced by various risk factors. One major factor is age, as children between the ages of 3 and 7 are most affected. During this period, the adenoids are active and contribute to growth and development. Overactivity or enlargement of the adenoids can cause airway blockages.
Chronic infection in the respiratory system, such as recurring colds, flu, or sinus infections, can lead to enlargement of the adenoids, which raises the risk of airway obstruction. Additionally, allergies causing inflammation in the nasal cavity can worsen the condition by obstructing the airway and making it harder to breathe through the nose.
A family history of respiratory conditions or a strong genetic component may increase the risk of developing adenoid face. Similarly, obesity, where excess body fat puts added pressure on the respiratory system, can result in breathing issues and adenoid enlargement.
Environmental factors such as exposure to secondhand smoke, pollution, or other irritants can cause damage and inflammation in the respiratory tract. This not only affects normal breathing but can also promote the growth of adenoids, exacerbating airway problems.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which involves stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus, can irritate the respiratory passages. This irritation may trigger inflammation and enlargement of the adenoids, increasing the likelihood of chronic airway obstruction.
Lastly, craniofacial abnormalities, such as a small jaw or a cleft palate, can impact the position of the tongue and surrounding muscles, leading to chronic obstruction of the airway. These abnormalities can also result in alterations to facial growth and development, compounding the risk of adenoid issues.
DIAGNOSIS
PHYSICAL EXAMS
The first step in diagnosing the adenoid face is a physical exam. During this exam, the doctor will carefully examine the mouth, throat, and nasal cavity to check for signs of enlarged adenoids.
Imaging Tests:
Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, may be used to evaluate the size and position of the adenoids and assess the severity of the obstruction.
These tests can also help identify any underlying structural abnormalities that may be contributing to the obstruction.
Allergy Testing:
If allergies are suspected as a contributing factor to enlarged adenoids, allergy testing may be recommended to identify any specific allergens that may be triggering the condition.
In conclusion, diagnosing adenoid face involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and specialized procedures, such as nasal endoscopy and sleep studies.
TREATMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF ADENIODS
In more severe cases, when symptoms like chronic mouth breathing, snoring, or even sleep apnea are present, a surgical procedure called an adenoidectomy may be necessary.
During this surgery, the adenoids are removed through the mouth or nose under general anesthesia. This procedure is recommended when the enlargement of the adenoids is significantly affecting the airway and leading to trouble with breathing or sleep disturbances.
For those with changes in their facial structure due to an adenoid face, orthodontic treatments like braces or palate expanders might be recommended. These treatments can help address skeletal and dental abnormalities, restoring the facial appearance and improving the function of breathing and swallowing. The goal of orthodontic interventions is to correct the underlying issues and reduce further complications in the future.
Lastly, if there are ongoing speech problems or swallowing difficulties, myofunctional therapy can help. This type of physical therapy focuses on improving the function of the mouth and throat muscles, which can reduce issues related to speech and swallowing, often linked with an adenoid face.
HOMEOPATHIC MEDICINES FOR ADENOID
Homeopathic remedies can offer effective support when dealing with enlarged adenoids. Several homeopathic medicines are known to treat this condition, providing relief from symptoms like nasal blockage and ear complaints. One of the most commonly used remedies is Agraphis Nutans, a natural medicine derived from the Bluebell plant, also known as wild hyacinth. This remedy is particularly effective when the adenoids become enlarged, causing issues like nasal blockage and deafness due to the swelling.
Agraphis Nutans
IT is often prescribed for cases where both the adenoids and tonsils are enlarged simultaneously. The effectiveness of this homeopathic remedy is noted for its ability to address the enlargement of the adenoids as well as ear complaints like deafness. Other homeopathic medicines, including Baryta Carb, Calcarea Carb, Sambucus, Ammonium Carb, Kali Sulphuricum, and Tuberculinum, are also recommended to treat various symptoms associated with enlarged adenoids.
These remedies help reduce inflammation and relieve the discomfort that comes with adenoids growing in size. When used properly, these natural medicines offer a gentle and non-invasive approach to managing adenoid issues, making them a great alternative to more aggressive treatments. Whether the issue is nasal blockage, ear complaints, or the physical changes caused by enlarged adenoids, homeopathy provides a holistic treatment option to consider.
Agraphis Nutans remains one of the most effective options for reducing enlargement and addressing ear problems caused by swollen adenoids, and it is a staple in many treatment regimens for those dealing with this condition.
- Belladonna, known for its ability to reduce congestion and ease discomfort associated with adenoid face.
Belladonna is typically indicated when the patient presents with dryness, thirstlessness, and symptoms of coryza (common cold-like symptoms). In many cases, the child might have mucus sputum mixed with blood, a clear indication that Belladonna’s properties can help soothe the irritation caused by enlarged adenoids. It effectively helps in reducing fever and promoting overall relief from the discomfort caused by these symptoms.
The usual dose of Belladonna for treating adenoid face is Belladonna 30, with 2 globules taken 3 times a day for about 3-4 days.
Calcarea fluorica,
- a well-regarded treatment for individuals presenting with an adenoid face. This condition often involves symptoms like mouth breathing, nasal obstruction, and a pale, waxy appearance. In my practice, I’ve seen Calcarea fluorica help alleviate these symptoms in a significant number of cases.
Typically, patients who require this treatment may also experience recurrent coryza, a form of persistent nasal congestion, along with dryness in the nasal passages and throat. An offensive smell from the nose or mouth is another common symptom. Many of these individuals also complain of discomfort, such as cheekbone pain or facial pain, which is often a direct result of the congestion and inflammation caused by the enlarged adenoids.
For Calcarea fluorica to be most effective, the usual dosage is Calcarea fluor 6X, with 2 globules taken 2 times a day on alternate days for a duration of about 1 month
IODUM
A remedy like Iodum is particularly effective in such cases, as it supports the normalization of metabolic processes, helping reduce the visible traits of the condition and easing related symptoms.
Administering Iodum 3X, at a dosage of 2 globules once a day for 10-15 days, can significantly help. This treatment is designed to not only address the outward symptoms but also promote internal balance. By targeting the root causes, Iodum facilitates long-term improvement, reducing the occurrence of conditions like recurrent dry coryza and easing breathing difficulties.
SILICEA
For children with adenoid face, a condition often marked by a delicate, pale appearance and persistent open-mouthed breathing, Silicea offers significant relief. These symptoms are typically accompanied by sensitivity to cold, making everyday activities uncomfortable.
Many patients also experience recurrent coryza that leads to throat infection after exposure to cold air. In some cases, the nose becomes obstructed, resulting in a loss of smell, which further worsens the quality of life.
Using Silicea as a homeopathic medicine helps address these challenges by targeting the root causes of recurring infections and physical discomfort. It is particularly helpful for children prone to colds, easing breathing difficulties and reducing nasal blockages. With a focus on holistic healing, Silicea supports better respiratory health while improving the overall comfort of those struggling with these symptoms.
SANGUINARIA
When children display an adenoid face, with a pale, sickly appearance, mouth breathing, and frequent headache, Sanguinaria Nitrica can be a helpful remedy. It is particularly effective in managing adenoid enlargement, which causes difficulty in breathing through the nose and leads to snoring or increased susceptibility to colds. Parents may notice symptoms like an obstructed nose with profuse watery mucus that causes burning pain. Early intervention with Sanguinaria Nitrica also helps prevent the development of adenoid faces in children.
Doctors might observe an enlarged turbinate as part of the hypertrophic process, signaling the need for timely care. Using Sanguinarium Nit 3X or 6C, at a dosage of 2 globules, 3 times a day for 5-7 days, supports improved respiratory health and reduces discomfort. This approach not only targets visible symptoms but also eases the breathing difficulties that come with this condition.
CONCLUSION
Adenoids are essential for immune defense but can lead to complications when enlarged. Timely diagnosis with imaging tests like X-rays and CT scans ensures effective treatment and better health outcomes. If you found this article helpful, please share it to help others learn more about adenoid-related issues!